#011
2020 AR/VR Industry Development Trends | Part 1: Augmented Reality
See current AR trends and how big corporations are utilizing AR

Augmented Reality (AR), when broken down into its technical composition, covers a wide range of fields and sectors. The required technologies may be slightly different if you look at it from a different perspective, or approach from a different angle. Hence, there is no one-size fits all solution for issues requiring AR technology.
In 2019, major companies such as Microsoft, Facebook, Apple, and Google have announced their investment in the R&D of the AR sector. Let’s have a look at the key trends in AR this year.
2020 AR Industry Trends | (I) Mobile Phones and AR Glasses Hardware Upgrade
3D sensing technology: ToF cameras pave the way for AR mobile applications
Simply put, ToF (Time-of-Flight) cameras uses the speed of light to calculate the distance between the different objects in the surrounding area and the user. Since 2019, more and more mobile phone manufacturers have begun using ToF cameras to replace depth-of-field lenses, to provide better photo effects, to the effect that ToF cameras are now considered a staple in most new-gen smartphones now. In addition to providing better quality camera images, the data from the sensors can greatly help with 3D imaging, thus making it more effective for improving AR experiences in the long run.
So, how does ToF cameras help with the AR experience? Before “placing” an AR object in the real world, spatial positioning needs to be done, so the device can determine the actual space in the surrounding environment. The function of the ToF camera is to help detect spatial distancing, helping to create an idea of what space is “real”, so that the AR object can be placed in as reasonable a position as possible, to the extent of achieving the occlusion effect, so that the AR object can conform to the special logic of the imaging in our brains, completely merging the virtual and real world objects.
ToF demonstrates the concept of “hardware first, software later”, as AR is expected to pick up in the coming few years. With major mobile developers such as Apple and Google demonstrating more interest in the AR sector, we are expecting more SDKs to come from these global conglomerates, bringing a more comprehensive AR experience at our fingertips.
2020 – The decade of AR glasses development
In 2019, many manufacturers released their own version of AR glasses, which we talked about in our article here. These companies include Microsoft’s Hololens 2, Google’s Glass Enterprise Edition 2, and many others such as Nreal, EPSON, Snapchat, Bose, NVIDIA, and so on, have come out and released AR glasses of their own.
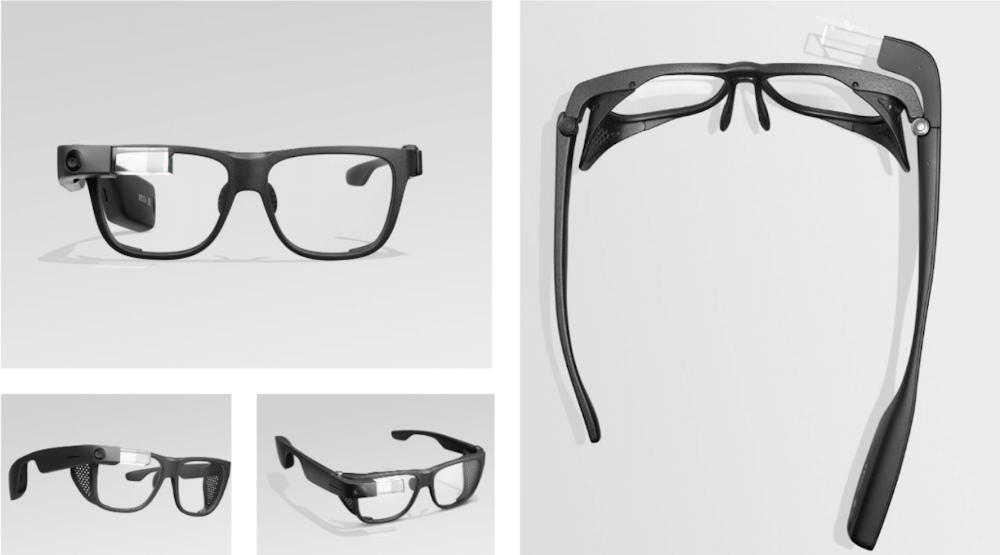

(Google Glass Enterprise Edition 2. Image source: Google)
In addition to that, there have been rumours about the research and development of AR glasses and tech from conglomerates such as Apple and Facebook, both who have yet to release any type of AR glasses. These rumours are enough to see various manufacturers regard AR glasses as the future of technology, something similar to the smartphones that we all own now, and make arrangements to incorporate technologies that support AR in their systems.
Currently, AR glasses are still mostly targeted at enterprise applications, instead of commercial applications, mainly used to improve work efficiency and optimizing system processes. Another reason is due to factors such as specifications, price, weight, display, and so on, which prevent AR glasses from penetrating into the consumer market – the battery life of AR glasses has always been a controversial issue.
However, Shenzhen Happy Valley theme park used a large number of AR glasses to create a themed festival experience in 2019. They pushed 2,000 AR glasses into consumer market on a large scale, using public charging stations to resolve this battery issue, leaving a lasting impression on both participants, and readers alike.
AR glasses, which allows for the superimposing of virtual elements into real-world scenarios, can gives the entertainment industry free reign to create more realistic gaming and branding experiences. In the future, it might become more commercialised like how VR has become, appearing more frequently in more industries.
2020 AR Industry Trends | (II) A Diversified Approach: Shared Experiences and Growing Popularity of Web AR
Cloud Anchor – Creating a shared AR experience
Currently, the AR experiences that we are familiar with only exist within one’s own mobile phone or AR glasses. How do we simultaneously let everyone experience the same AR content? That is the million-dollar question.
In order to provide a cross-platform, shared AR experience, Cloud Anchor technology was born. The principle of Cloud Anchor similar in behaviour and function to anchors, but are hosted on the cloud. It is a 3D model constructed through the mobile vision, comparing and filtering abnormalities to find and analyse the positioning, so that multiple users can interact with the same AR object using their own devices.
Pokémon GO launched a group photo function in December 2019, which uses Cloud Anchor technology. The trainer can see the Pokémon that they and 2 other users have summoned on the same screen, easily interacting with the Pokémon and the users, taking fun AR photos together. The continuous advancement of Cloud Anchor technology will eventually allow Pokémon trainers to summon their own Pokémon to fight with an opponent trainer’s in real life.
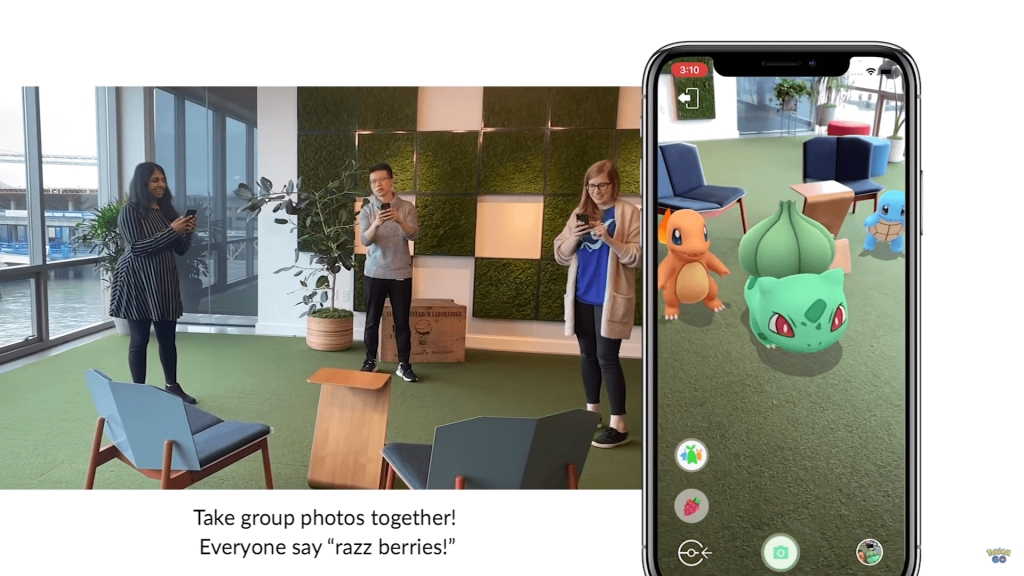
(Pokémon GO uses Cloud Anchor technology, allowing users to access the same AR content on their own devices. Image Source: Pokémon GO)
Presently, the stability of the anchor point data synchronisation on the cloud still needs to be strengthened, and the storage data of the anchor point data is not enough. There are still certain limitations, such as the need to avoid having repeating patterns in the surrounding areas, avoid reflective surfaces, and so on. But even so, Cloud Anchor technology can provide a shared AR experience that is fully integrated with the real world, giving the AR objects a new dimension, as compared to virtual content that can only be seen and experienced by oneself. A shared virtual experience is more integrated into the real world, and when these virtual objects can be seen and experienced by everyone in the surrounding area, it strengthens the phenomenon of the interaction, resulting in a more realistic and innovative AR experience for all involved.
WebAR for advertising and entertainment
WebAR is great for its download-free and quick launching capabilities. Still in the early stages of its innovation, it still can’t run complicated AR experiences yet. However, you can directly use it for simple applications through a URL or QR code, hence it is a popular choice for advertising and marketing, greatly reducing the barriers of entry for many users.
Since Chrome version 79, Google had begun to provide WebXR support, expanding their degree of support from Chrome version 81 onwards, including the WebXR Hit Test module. Despite many browsers not supporting WebXR yet, there are also limitations on browsing and permissions. But with Google taking the lead, we see an increase in browser support for these technologies, providing AR developers a wider range of arsenal, compared to purely dealing with mobile browsers. This means that with this upward trend in motion, there will definitely be more ways to experience WebAR in the coming future.
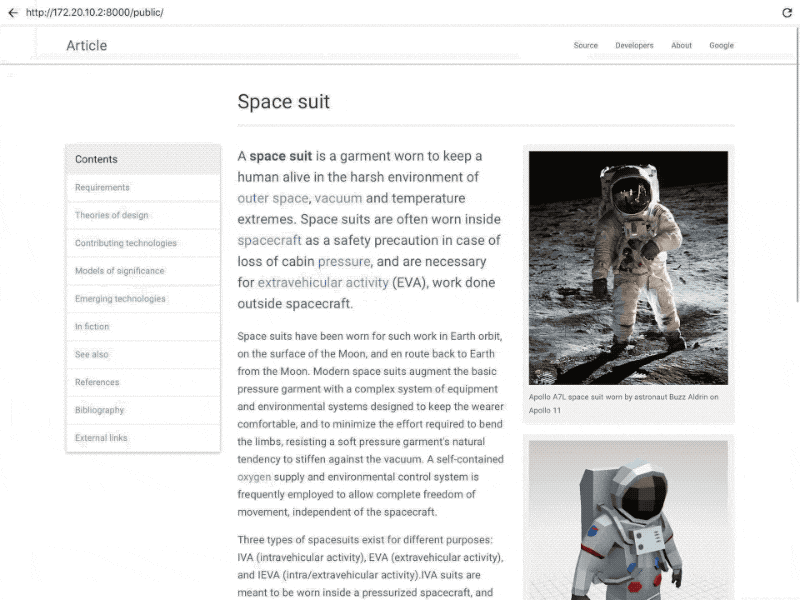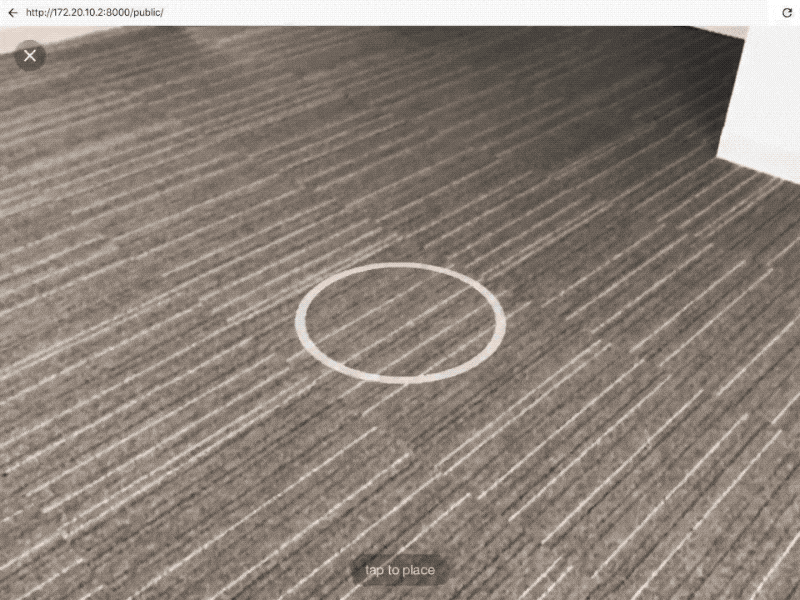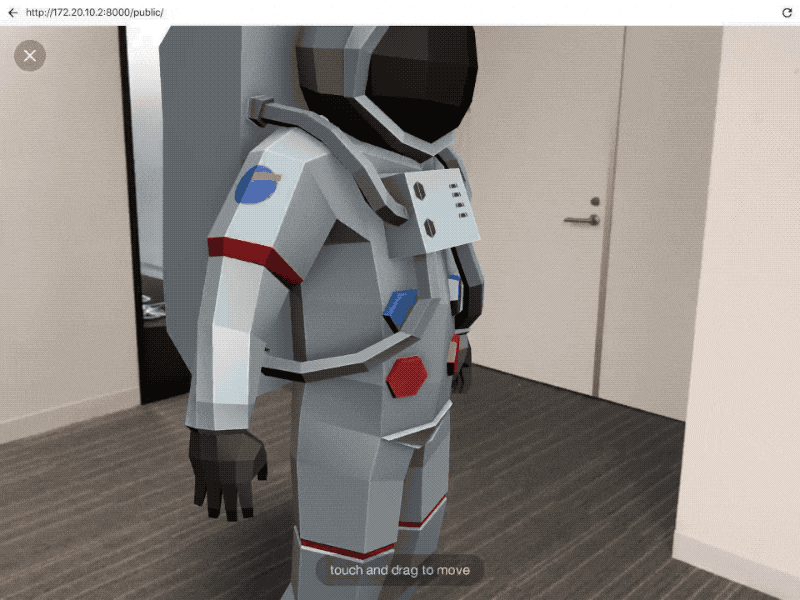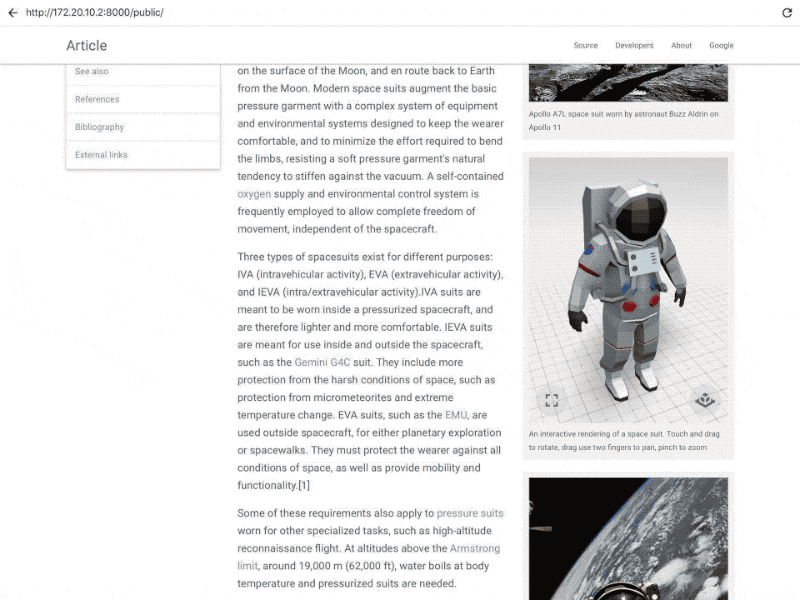
(Google’s WebAR display screen. Image Source: Google)
2020 AR Industry Trends | (III) Developments in 5G Applications
With many countries announcing the commercialisation of 5G in 2020, we see mobile phones companies who successively launched devices that support 5G internet access. With its greater bandwidth, giving higher download speeds – eventually up to 10 gigabits per second (Gbit/s) – 5G has the world heatedly discussing how this new technology can benefit and be implemented in industries such as AR/VR, AI, IoT, and so on.
As AR technology needs to transmit a large amount of visual data and perform complex calculations, the speed and bandwidth of the commercialisation of 5G will indirectly help AR to become more widely accepted, as it runs at a more efficient pace. Mobile support for 5G means that a large amount of visual data can be obtained faster, simultaneously reducing the downloading and load time of an AR experience. Through creating a seamless end-to-end experience, giving a stronger impression of the virtual and real-world integration.
At the end of 2019, Qualcomm also released the world’s first AR/VR processor platform that supports 5G networks – Snapdragon XR2, becoming one of the pioneers of integrating Cross Reality (XR, an umbrella term encompassing AR, VR, and MR), with 5G technology. We predict that in the future, with the integration of XR and 5G, comes more application cases for new immersive reality technologies. One day, we might even be able to transfer information and data quickly, via 5G to the Cloud, then back to the AR glasses for display, greatly streamlining the use of AR glasses, helping with the commercialisation of the glasses.

(Image source: Qualcomm)
Going back to the progress of global 5G deployment, it is still in the early stage and hardware support is not yet very mature. It can be expected that AR combined with 5G applications in 2020 will be mainly exemplary applications in specific fields.
To summarise, the adoption of AR is slowly, but steadily growing, especially more so when there are breakthroughs such as in the environment, hardware, and software. Industries such as marketing, manufacturing, tourism, medical care, finance, retail, catering, sports, publishing, media, exhibitions, education, and many more are starting to integrate AR in their current offerings, to give users a new, more memorable experience. As technology evolves, AR too will evolve, becoming an brand new platform for innovative communication.
